
Post
5S GUIDE - A LEAN MANUFACTURING TOOL
Post
CIRCULAR MANUFACTURING: THE RULES OF THE CIRCLE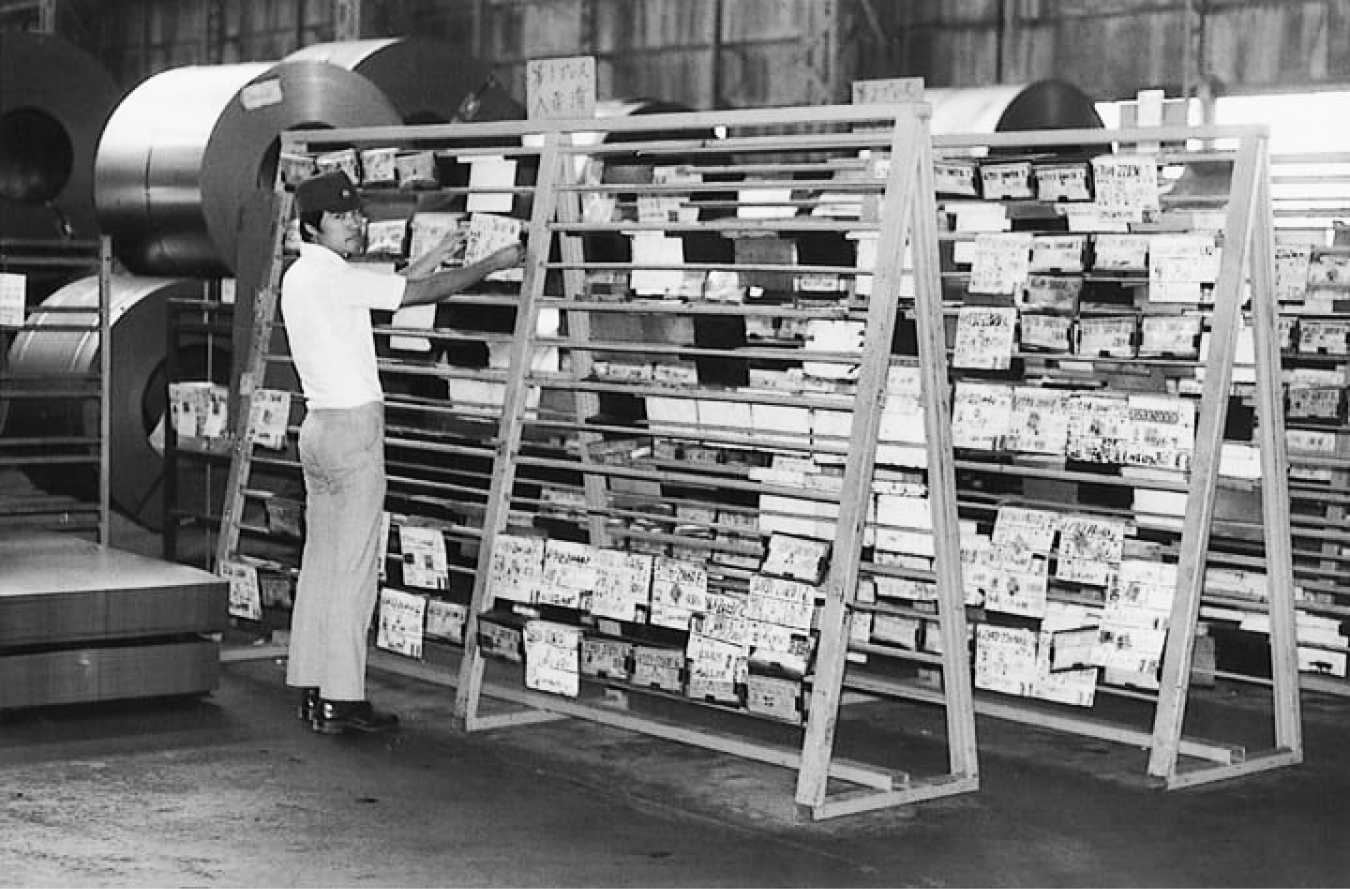
Post
HOW EKANBANS OPTIMIZE YOUR MATERIAL REPLENISHMENT PROCESS
In the manufacturing realm, optimizing for efficiency while meeting ever-evolving market demands is critical. Enter Heijunka, a Japanese technique of “leveling production”. Renowned as the backbone of the Toyota Production System (TPS) and the foundation of Lean methodology, Heijunka serves as a beacon for operational excellence.
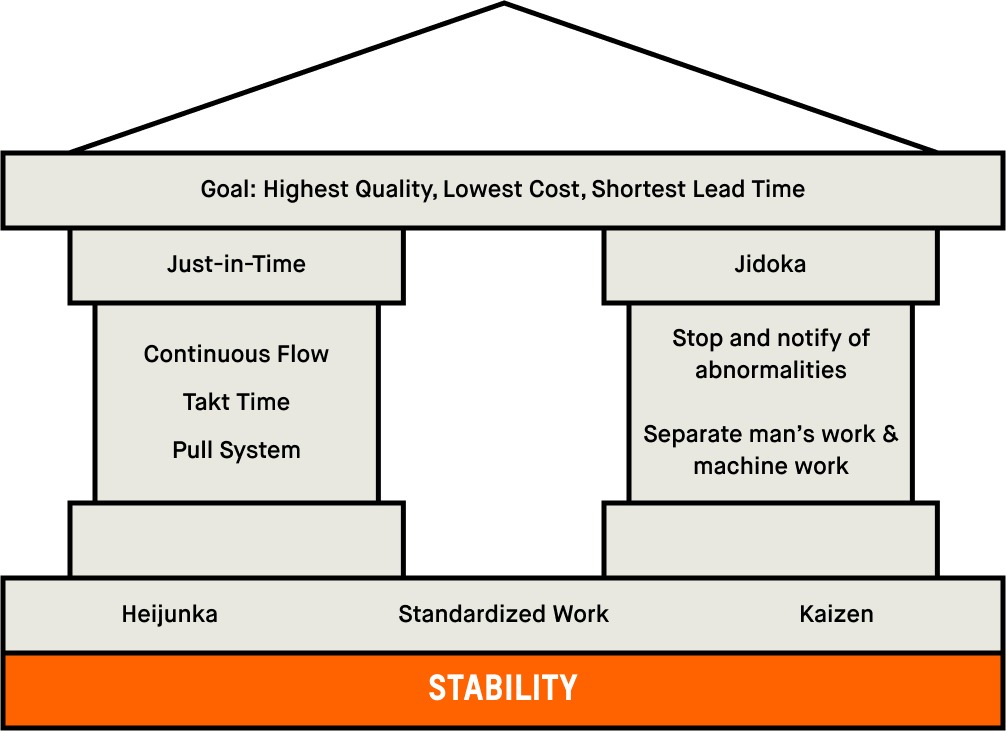
Heijunka, pronounced “hey-june-kuh”, is more than just leveling production; it represents a philosophy to combat waste, align production with actual demand, and ultimately, streamline operations. Originating as an essential pillar of the TPS, Heijunka’s inception was aimed at addressing the unpredictabilities and inefficiencies resulting from erratic production schedules and fluctuating customer demands.
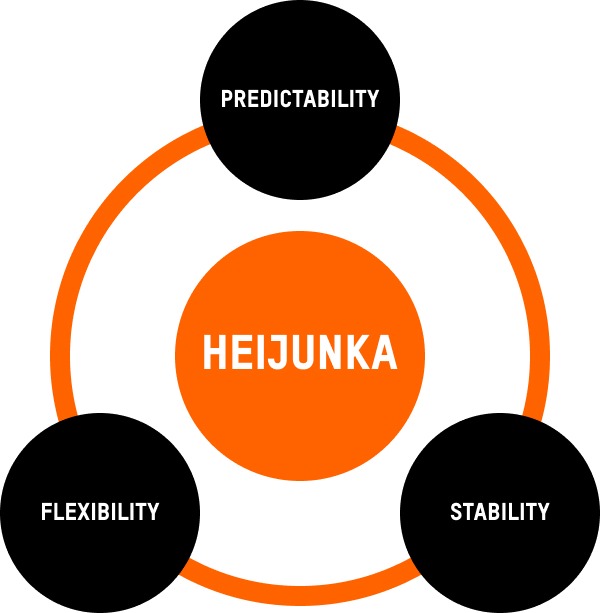
By integrating the principles of Heijunka, manufacturers are empowered to craft a balanced and rhythmic production cadence. This harmonized approach reduces lead times, ensures high-quality output, and optimizes resource allocation, thus bolstering overall operational efficiency.
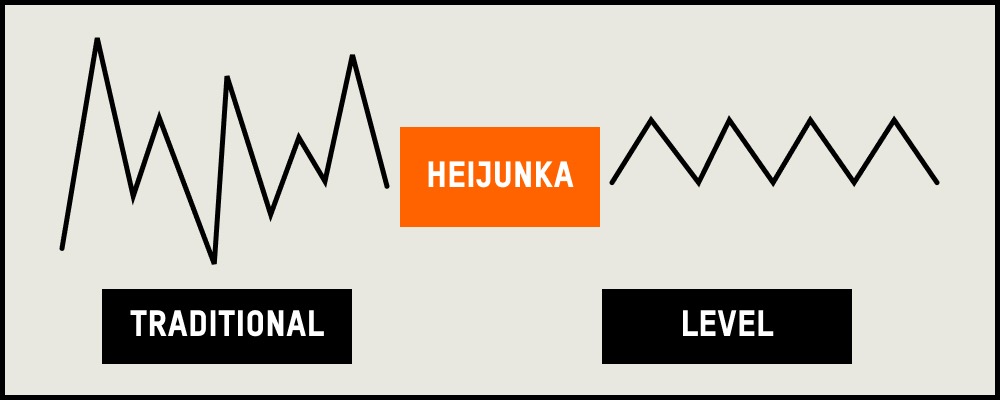
Demand Smoothing: Central to Heijunka is the principle of demand smoothing, ensuring production orders are evenly spaced, mitigating the risks of abrupt demand fluctuations. It addresses challenges like overproduction during demand peaks or resource underutilization during lulls.
Mixed-Model Production: Unlike traditional manufacturing that emphasizes large batches of a single product, Heijunka promotes mixed-model production. It’s a holistic approach, producing varied products in small batches, aligning with changing customer preferences without accumulating unnecessary inventory.
Takt Time Integration: Central to Lean methodology, takt time — the rate at which a product must be produced to meet customer demand — is interwoven into Heijunka. This synchronization ensures that manufacturing processes are consistently paced and optimized.
Waste Reduction: Heijunka’s strategic distribution of production orders significantly trims waste. This includes overstock, overproduction, and the mismanagement of resources. By eliminating these inefficiencies, businesses can realize cost savings and enhanced resource stewardship.
Enhanced Flexibility: The mixed-model production championed by Heijunka enables manufacturers to rapidly pivot in response to market shifts or evolving customer preferences. This dynamism ensures production remains in sync with real-time demand.
Employee Empowerment: A predictable Heijunka-driven rhythm reduces the chaos and stress stemming from sudden production shifts, fostering a healthier, more engaged workspace.
A successful Heijunka implementation can be further enhanced with the integration of the Kanban system, a visualization tool to improve workflow and manage work-in-progress.
Demand Forecasting: Start by analyzing past demand trends and market trajectories to craft an accurate production roadmap.
Standardized Work: Create consistent work procedures. This uniformity ensures tasks are executed uniformly, promoting a consistent production flow.
Kanban System Integration: Meld the Kanban system for material resupply. It complements Heijunka by ensuring the smooth flow of materials and matching production rhythm. Kanban visualizes the workflow, makes policies explicit, and fosters continuous improvement — all aligned with Heijunka’s goals.
Collaboration and Communication: Foster effective intra-departmental communication. This synchronization is key to aligning production plans and swiftly responding to any changes.
In our rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, Heijunka stands out as a robust tool for optimizing production workflows. Combined with the Kanban system, this synergy offers unparalleled potential to transform manufacturing practices. As businesses worldwide strive for operational excellence, Heijunka and Kanban might be the duo driving them to new efficiency frontiers.
