
Post
TOP 6 TOOLS FOR CUTTING
Post
WHY YOUR WORKPLACE REQUIRES A FLEXPIPE CRIBWhen designing a modular cart, make sure to keep efficiency and ergonomics top of mind. Each feature can contribute to reducing wastes. Lack of proper planning can result in sub-par performance and employee frustration. To make the experience of designing your cart easier, read on for relevant information and helpful tips on each of the cart’s components.
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
 5-6h
5-6hReady? Let’s begin – it comes down to 6 essential steps.
![]()
Download the image version of this guide
It’s essential to accurately define your needs when designing your cart as its features will enable you to work as efficiently as possible while reducing any unnecessary movements.
When defining your needs, ask yourself the following questions:
Now that you’ve established your needs, it’s time to select your cart’s various components. Choose each of them wisely and you’ll be rewarded with a cart that will move its contents efficiently. You’ll find below each component’s features along with pointers to keep in mind when designing your cart.
Casters come in different diameters, shapes, and fastening systems. The choice of casters is vital as you’ll want to pick those which will move your cart smoothly no matter its size or load capacity. That said, the bigger the wheels, the smoother your cart will roll.
Below, you’ll find a description of 2 types of casters which are most frequently used in modular carts.

Stem casters (“rod caster”) with an adapter are recommended for:
Note that 4-in. diameter stem casters are suitable for carts which cover a distance ranging from 30 to 50 feet, and that will be used from 20 to 50 times a day.

Plate-mount casters are recommended for:
To make your design process simpler, all casters sold at Flexpipe are equipped with a precision ball bearing and a non-marking gray thermoplastic rubber (TPR) sole. Swivel casters are all equipped with a brake that can be removed if necessary. Note that SKUs beginning with the letter “E”, such as EW-3ESB, are antistatic wheels.
TIPS AND TRICKS
For carts that will go outside, roll on ramps or damaged floors, it’s preferable to use casters with a diameter of 6 in. or more.
Government health and occupational safety centers recommend that the use of carts be limited to a travel distance of 100 feet, up to 200 times per day for a single person. If you plan on using your cart more than 200 times per day, why not consider using a motor vehicle (tugger) to pull your Flexpipe carts?
MORE INFORMATION
See all casters we have in-stock!
Caster positioning is essential to make sure that your cart is stable and easy to maneuver. As a rule, it’s preferable to install 2 fixed casters and 2 pivoting casters on your cart. The swivel casters will be placed on the end where the cart’s handle is located, so you have greater control when steering the cart.
If the cart is to be used in a small area (e.g., a tight workspace), we recommend putting on 4 swivel casters.
The distance between two casters should ideally range from 24 in. to 48 in. If the distance exceeds 48 in. (for larger carts), add 2 casters in the center.
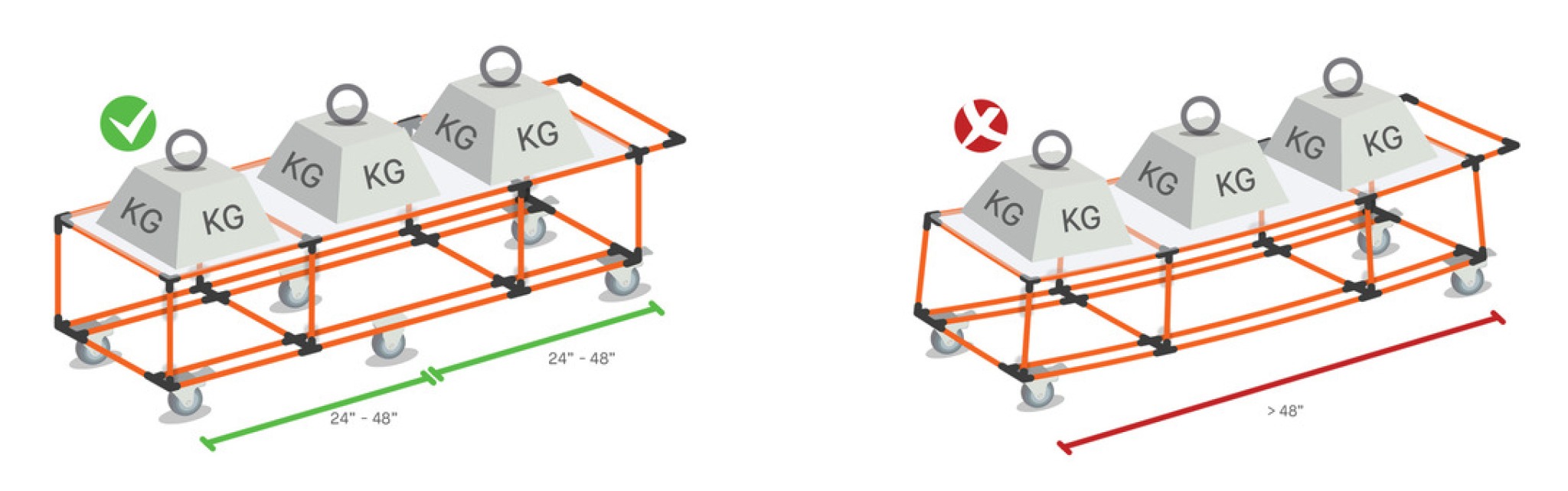
Here is an example configuration for a 6-caster cart:
TIPS AND TRICKS
The casters do not necessarily have to be at the end of the cart to maintain the required 48-in. spacing; you can simply bring them closer to the center – just as long as the cart remains stable.
The positioning of the casters can vary if the cart is to be pulled by a tugger.
Here is a detailed video about our caster:
Choosing the dimensions of the cart is mainly contingent on the parts that it will transport. You’ll want to make sure that there’s a place for everything and that everything is in its place!
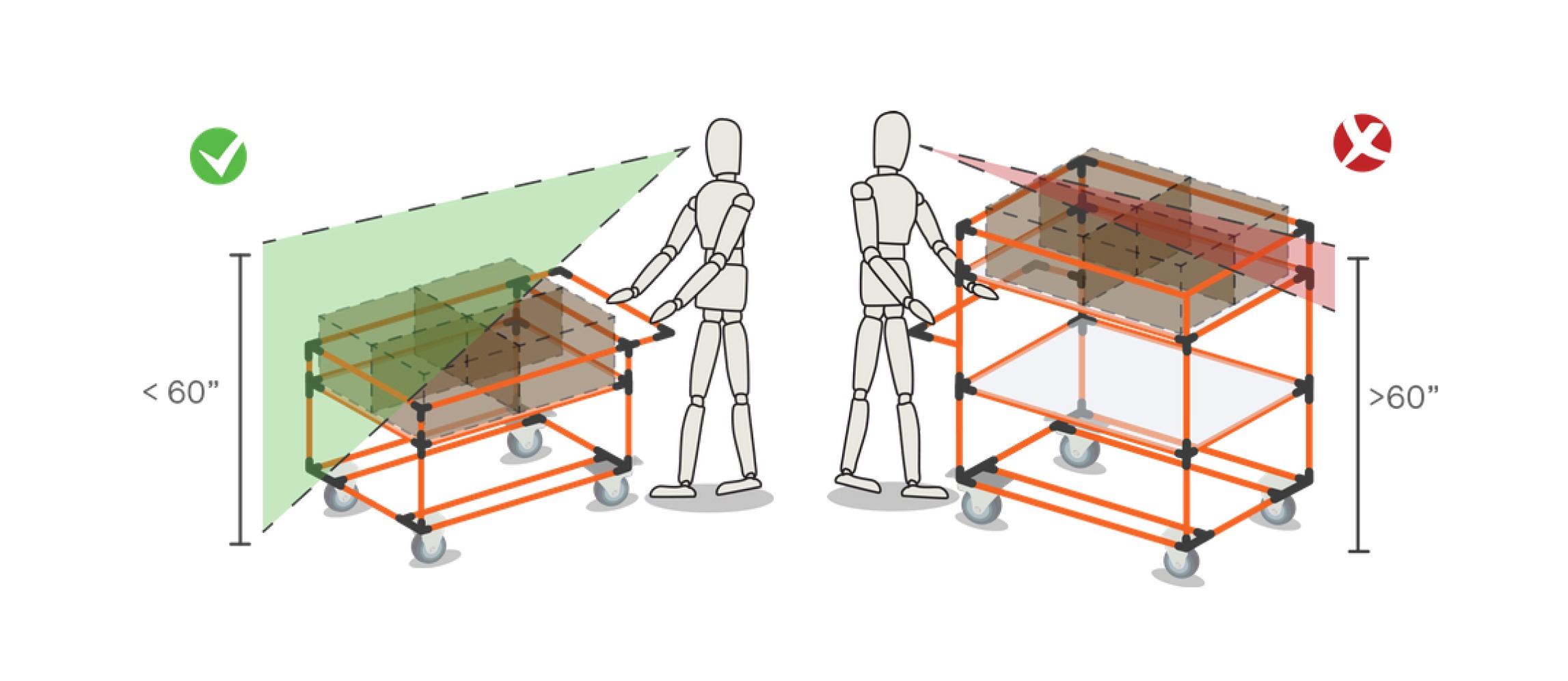
Do make sure to keep in mind these considerations:
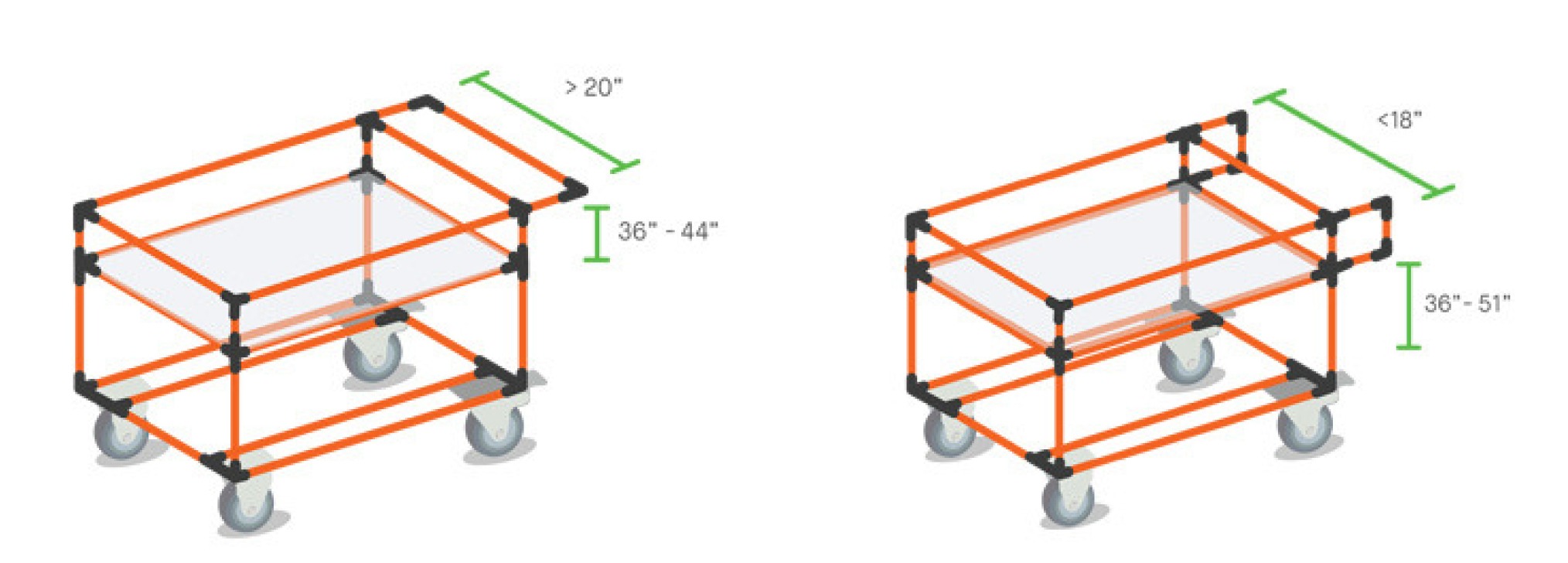
The handle is a key element, especially for ergonomic concerns. You’re going to be touching that handle frequently, so it’s wise to give some serious thought to its position and length.
Here a few pointers:
There are 2 possible positions for the handles: vertical and horizontal. Note that the height at which the handle is installed can vary according to the cart’s purpose.
Shelves can be an added plus to the cart’s overall functionality. Whether long or short, shelves can be tailored to fit your cart for a specific need. The most common surfaces on carts are ¼-in. HDPE (“High-Density Polyethylene”) and ½-in. HDPE.
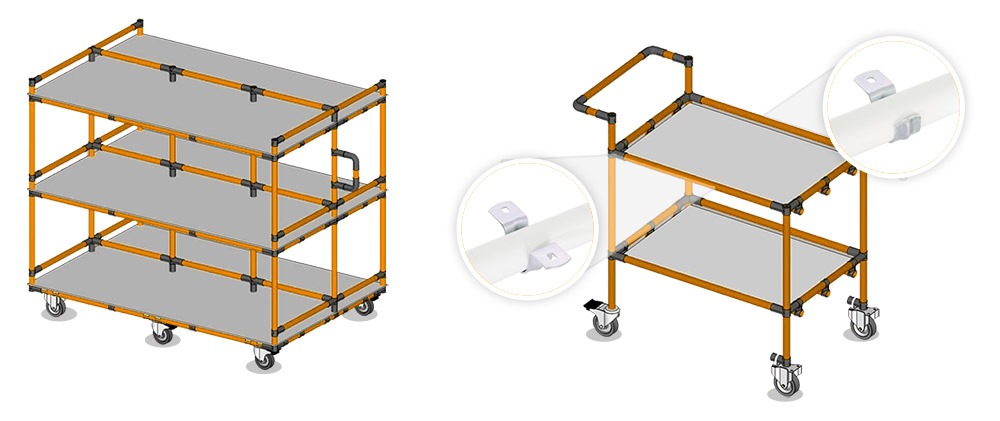
Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
It’s worth noting that tubes or conveyors can do precisely the same job as shelves, and can be more budget-friendly, too. Remember to check if contouring is necessary to prevent your pieces from falling off the cart. If you do need some, you can embed the ¼-in. or ½-in. surfaces by using #AI-CORNER corner brackets. If this is insufficient, add tubes to the desired height to build the contour.

So as you can see, each of the 5 components listed above has an important role to play in ensuring that your cart moves around as smoothly as possible. If one of the elements is not a perfect fit for your needs, it will negatively impact your cart’s – and your employees’ –performance.
Ready to build your cart? You can order the parts online.
Need a second opinion about your cart’s design?
Send your sketch to your project manager for validation. He will follow up with you to finalize the design.